Introduction
This article deals with external wire rope wear and the rejection criteria detailed within ISO-4309.
Wear occurs in all running crane rope subject to contact with metal sheaves, drums, and other guiding components. (For information on the causes of wear, click here)
1. Mark I Eyeball
External wear is usually visible on the surface of wire rope. However, in the case of light wear, this may be harder to spot. With conventional, as opposed to compacted ropes, a visible flattening of the wires can be observed.
As shown in the diagrams below, the gap between the apex of the wires reduces with increased wear.
Important: This method is less effective when dealing with wire rope with compacted outer strands.
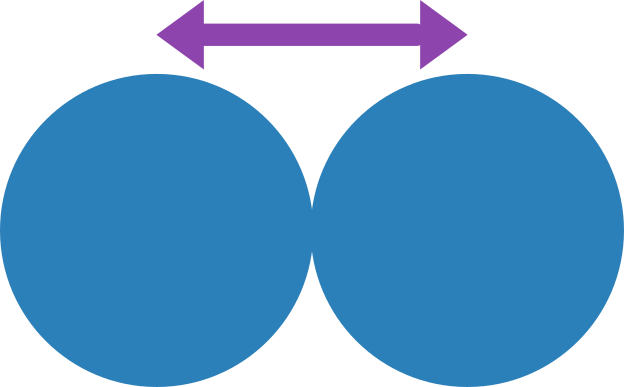
No Wear - Diagram Illustrating the large apex gap.
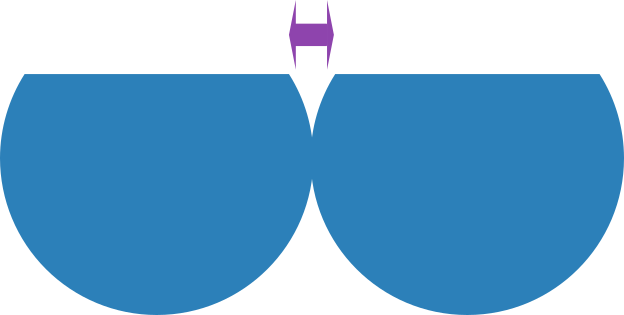
Heavy Wear - Diagram Illustrating the reduced apex gap.

Severe Wear - Diagram Illustrating the lack of an apex gap.
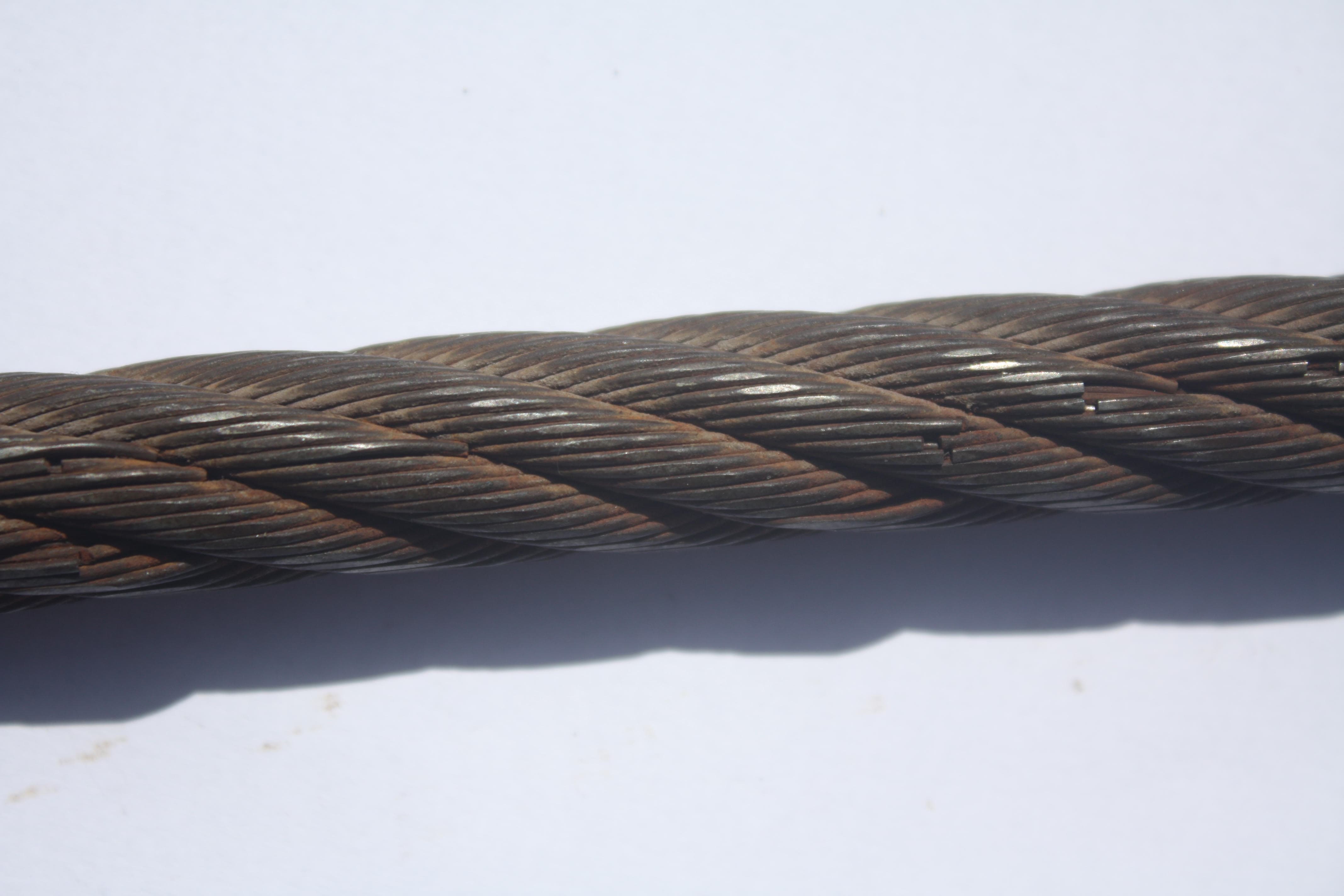

Light Wire Rope Wear
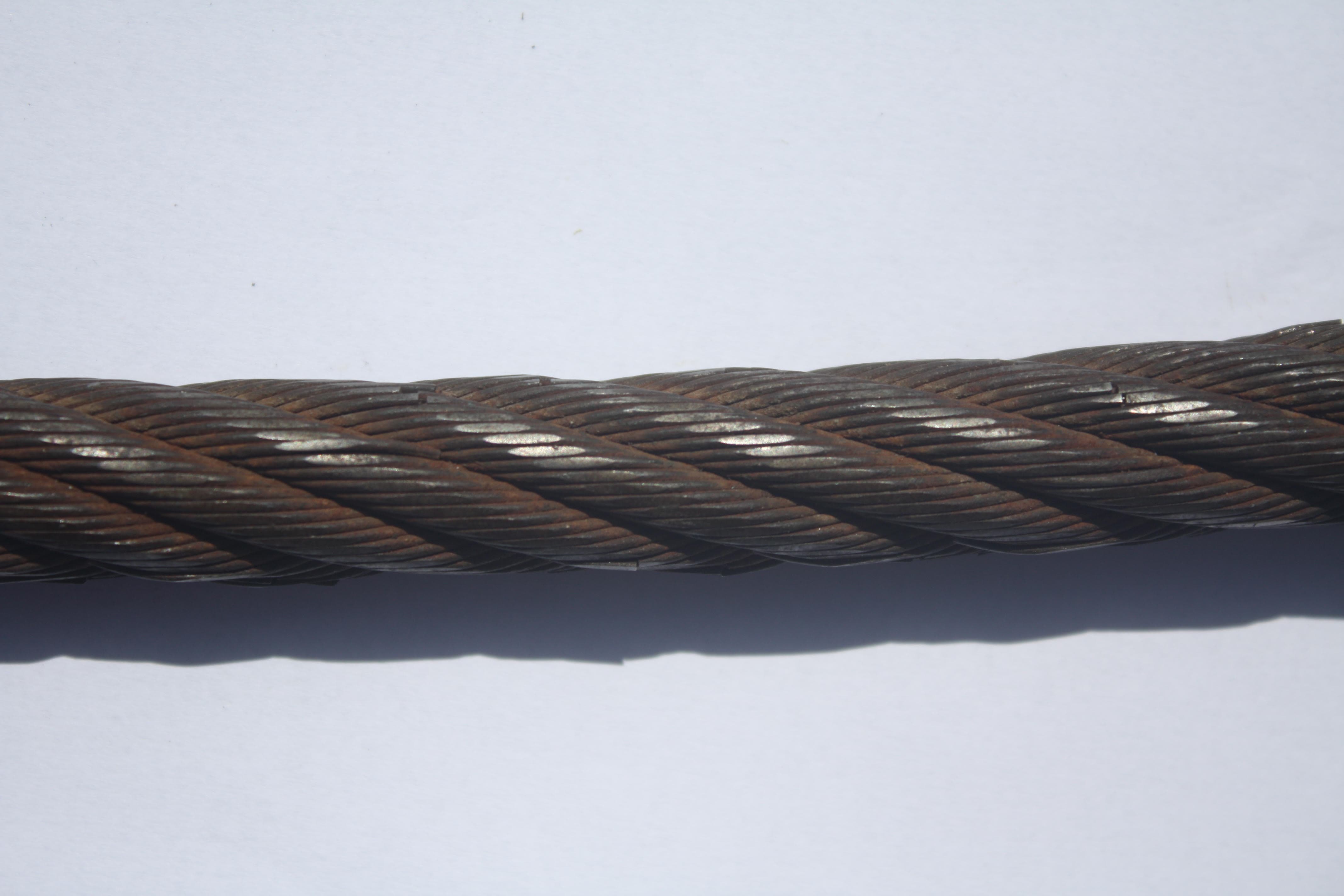

Heavy Wire Rope Wear
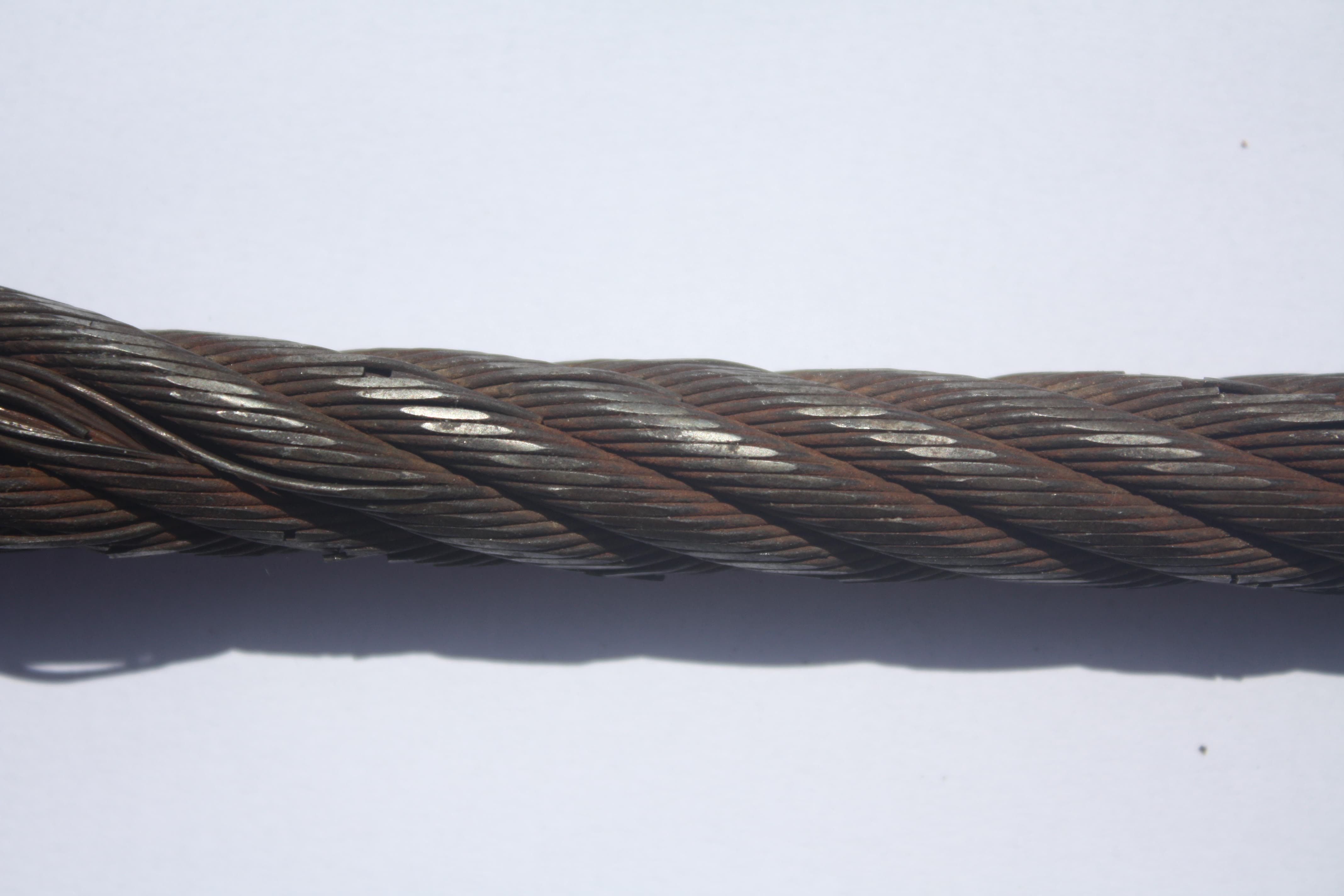

Severe Wire Rope Wear
2. Diameter Measurement
Although the method above is a quick and effective way of assessing external wear, measuring the rope's diameter should always be the preferred option.
ISO 4309 details the percentages for discarding a wire rope due to wear alone. The list below shows the discard criteria for diameter loss.
- 6 and 8 strand ropes with Fibre Core- 10%
- 6 and 8 strand ropes with Steel Core- 7.5%
- Rotation Resistant Ropes- 5%
To obtain the percentage diameter loss, subtract the measured diameter from the reference diameter, divide this number by the nominal diameter, and multiply the result by 100. (Rope IQ performs these calculations automatically.)

Formula to calculate loss of diameter in wire rope.

Diagram Illustrating the correct way to measure wire rope diameter.
3. Magnetic Resonance Testing
Non-Destructive examination of ropes is also an effective way of determining the level of wear.
The discard criteria for loss of metallic cross-sectional area over a length of 30 diameters is 10%.
Conclusion
If not strictly monitored, wear in wire rope can be especially dangerous. This article provides three effective methods of identifying wear and the appropriate discard criteria.
Although Method 1 is useful for identifying wear, we recommend only using it as a quick check and not to make discard decisions.
Thanks for reading! If you enjoyed the article, be sure to give the Rope IQ LinkedIn page a follow so you can keep up with our updates!
Again, thanks for reading,
The Rope IQ team.
Want to find out how our software can help your business?
Request a quick 30 minute demo to find out.
Request a Demo